Ruptured appendix also known as peritonitis is a potentially fatal medical condition that is characterized by acute abdominal pain. Ruptured appendix is the end result of appendicitis which is basically the inflammation of the appendix a small worm shaped tube attached at the beginning of the large intestines, due to blockage.
If the blockage continues, the inflamed cells start dying out due to bacterial infection and a lack of blood supply and if left untreated Appendicitis rapidly develops into the fatal and extremely painful peritonitis. This condition is fatal because in most cases when it occurs; highly infectious intestinal fluids such as pus spill into the abdominal cavity and sometimes into the blood supply.
Ruptured appendix and appendicitis are the most common pediatric medical emergency that more often than not requires abdominal surgery. In most cases appendicitis affects people in their teens and early twenties, with males reporting a high occurrence of appendicitis compared to females of the same age group.
Further there are fewer recorded cases of the occurrence of appendicitis in either the elderly or in children below the age of two years. Moreover according to medical journals there is a high occurrence of appendicitis in developed countries as opposed to developing or underdeveloped countries.
Causes of Ruptured Appendix
Although the appendix has no obvious function in the human body it sometimes becomes infected and if left untreated these infections regularly cause fatalities. Just like its function in the body the main causes of appendix rupture are not very clear as there is no definitive single causing agent.
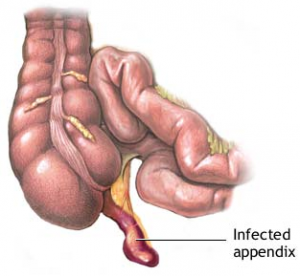
But in general ruptured appendix is widely considered to be the end result of an inflamed and highly infected appendix due to blockage. This blockage is mostly caused by foreign bodies such as worm infestations or the popular calcified fecal deposits also known as fecaliths.
In most scientific studies featuring the appendix, fecaliths feature prominently. The occurrence of fecaliths is in most cases directly connected to the probability of appendicitis in most cases.
For example people in developing countries have reported higher deposits of obstructing fecaliths and a higher occurrence of appendicitis as opposed to people in the under developed countries. Fecaliths which occur as a result of extended digestion durations usually puts people at a higher risk of a ruptured appendix.
Ruptured Appendix Symptoms
In most cases a ruptured appendix presents in a succession of symptoms such as acute abdominal pain, nausea, fever, a fast heart rate and a reduction in the white blood cell count. The most important symptom of a ruptured appendix or appendicitis is acute pain normally starting around the navel.
As the inflammation of the appendix advances the pain moves lower and to the right at the same time becoming more acute such that any movement or sudden pressure to the abdomen causes excruciating pain.

Over time the abdomen becomes rigid and tender and the symptoms become more severe and consistent; at this stage there is a high likelihood of getting a ruptured appendix.
Further a lack of appetite and constipation coupled with diarrhea and fever are usually the most definite indications of a ruptured appendix as the infected intestinal fluids leaking from the appendix seep into neighboring organs and tissue.
In some rare instances these symptoms may disappear within twenty four hours and recur at a later date a condition known as chronic appendicitis.
One of the ruptured appendix symptoms usually involves the deposition of harmful and highly infected intestinal materials such as fluids and fecaliths into the adjoining abdominal cavity.
As such there are very many complications such an inflammation of the adjoining membranes lining the abdominal wall and neighboring organs due to the accumulation of pus or bacteria within these tissues.
Further in some cases the intestines are blocked due to the inflammation of the appendix which interferes with the regular workings of the intestinal muscles. In most cases sepsis also occurs due to the leaking of the harmful infected fluids from the ruptured appendix into the blood stream a potentially life threatening condition.
Ruptured Appendix complications

Although appendectomy or the surgical removal of the appendix is one of the most straight forward procedures, with very few possible ruptured appendix complications and a mortality rate of about one in every a thousand patients, removing a ruptured appendix considerably increases the possibility of complications in most cases.
According to studies carried out in different countries the mortality rate after the removal of a ruptured appendix is estimated at seventeen people in every a thousand. This is mostly due to the risk of sepsis and the fact that all the infected materials from the appendix and the adjoining tissue have to be completely eliminated; normally a very challenging task for the surgeons.
Ruptured Appendix Recovery
After the removal of the appendix, most patients report a fairly smooth recovery. Apart from a dull pain that most people report mainly because of the incision made during the surgery, most patients make a fairly quick recovery ranging from a few days up to about three weeks
Enjoyed Ruptured Appendix? Share it with your friends so they too can follow the Superfoodsliving journey.
Share on Pinterest
